Ultrapure water is water in which conductive ions, colloid, organic matter, etc. are all removed, and its water resistivity is greater than 18 MΩ·cm (25 ℃). The ultra-pure water system generally adopts pretreatment technology, reverse osmosis technology, electric salt removal technology and post-treatment, and at the same time, it is equipped with auxiliary treatment such as ultraviolet lamp and TOC device.
The process of preparing ultra-pure water
The process of preparing ultra-pure water is: tap water → pretreatment system → multi-stage high-pressure reverse osmosis system →EDI electric desalt system →TOC device → polishing mixed bed system → water point. In the preparation process, the water pump is used as the power source, and the storage tank at all levels should ensure that the system water pump can operate safely and stably. The addition of different treatment levels of filters in individual parts can ensure the quality of the water produced.
At the same time, during the operation of the filter, various agents can be added to adjust the pH value of the water, reduce the residual chlorine in the water, and slow down the scaling speed of the RO membrane. In winter, in some areas with low temperatures in the north, heat exchangers will be added at the inlet of the pretreatment system to make the water temperature of the tap water meet the requirements of the water production process of the equipment.
In addition, in the ultra-pure water tank, it is very important to use nitrogen to isolate the water from the outside medium, which can ensure that the prepared ultra-pure water is not secondary pollution by air.
The importance of pretreatment systems
1. Water inlet requirements of RO membrane
In the process of preparing ultra-pure water, the RO system is the most critical. The normal operation of the RO system can ensure the operation safety and water quality of the entire pure water equipment. In the process of preparing ultra-pure water, the RO system has certain requirements for water intake, which are as follows:
Silt density index (SDI value) <4.0;
Turbidity (NTU) <1.0 100 T/h;
Organic content (COD) <1.5 mg/L;
Residual chlorine content < 0.1mg /L (actually controlled at 0 mg/L);
When dissolved oxygen >5 mg/L, iron content <0.05 mg/L;
SiO2<100 mg/L in concentrated water;
LSI, pHb-pHs<0;
Sr, Ba and other ions are easy to form insoluble salts, Ipb< 0.8Ksp.
2. The role of pretreatment system
Before entering the reverse osmosis system, the pretreatment system should be used to remove the residual chlorine, large suspended particles and flocculated colloidal impurities, organic matter, oxide, organic matter, heavy metals in the water to reduce the COD value and SDI value.
In addition, calcium, magnesium, barium, sulfate, silicate and carbonate plasma in water can be combined with the above ions to form macromolecular particles by adding scale inhibitor, and then discharged in the form of concentrated water in the reverse osmosis device.
(1) The impact of abnormal system operation on RO membrane
From the relevant content of pretreatment, it can be seen that before entering the RO membrane, the vast majority of polymer harmful substances will be removed by the pretreatment system. If the pretreatment system is defective and many of the reverse osmosis water intake indicators are not up to standard, it will lead to irreversible physical and chemical damage to the reverse osmosis membrane elements, which will greatly shorten the service life of the reverse osmosis membrane elements. There are several factors that affect the service life of reverse osmosis membrane elements:
RO membrane fouling;
RO membrane is polluted by metal oxide;
Suspension blocking RO membrane;
Colloid, organic matter and microorganisms are polluted, resulting in an increase in effluent COD.
(2) The impact of system anomalies on reverse osmosis ultrapure water systems
When the pre-treatment system runs abnormally, it will affect the operation of the entire reverse osmosis ultra-pure water system, which is reflected in the following three aspects:
Reduce the water yield and quality of reverse osmosis ultrapure water system;
Increase the water and electricity energy consumption of reverse osmosis equipment operation;
Increase the operating cost of water treatment, including scale inhibitors and other water treatment agents.
The working principle of ultrafiltration system and activated carbon system
In the actual production process, the common pretreatment systems include ultrafiltration system and activated carbon system. The ultrafiltration system is composed of disk filter and ultrafiltration device. The activated carbon system is composed of multi-media filter and activated carbon filter.
1. The working principle of ultrafiltration system
The working principle of the disc filter is to achieve surface filtration and deep filtration through a compressed plastic disc. It is mainly used to remove sediment and other large particles in the water. Ultrafiltration is a pressurized membrane separation technology, that is, under a certain pressure, the small molecule solute and solvent pass through a special membrane with a certain aperture, and the large molecule solute (molecular weight of 10 000 ~ 30 000) cannot pass through, remaining on one side of the membrane, so that the large molecule substance is partially purified. The working principle of the ultrafiltration system is shown in Figure 1.
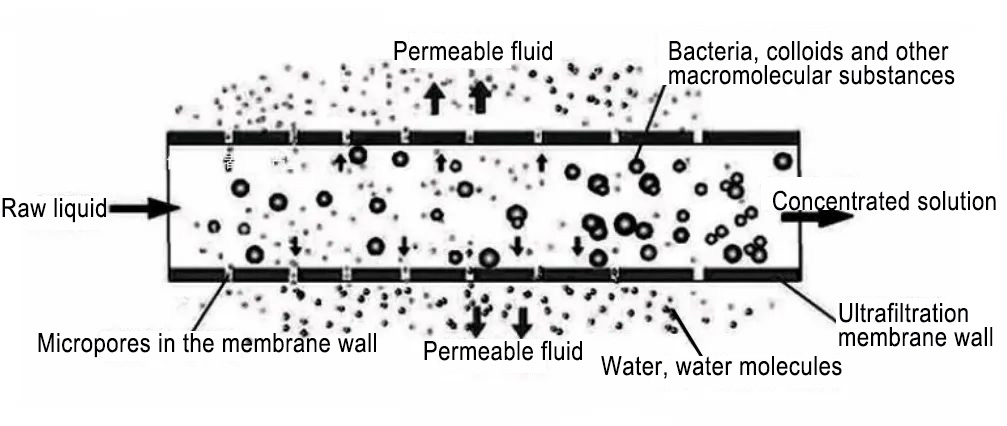
2. Working principle of activated carbon system
Multi-media filter is the use of one or several filter media, under a certain pressure, so that the water with high turbidity through a certain thickness of granular or non-granular filter materials effectively remove suspended impurities, so that the water is clarified.
Commonly used filter materials are quartz sand, anthracite and manganese sand, etc., which are mainly used for water treatment turbidity removal, softening water, pre-treatment of pure water, etc., SDI value can reach 3 or less. After the water filtered out by the multi-media filter enters the activated carbon filter, because the activated carbon filter is equipped with quartz sand as the base bed and activated carbon as the filter material, the activated carbon of the filter material can remove impurities such as residual chlorine, organic matter and suspended matter in the water through its own gap under the action of Van Der Waals force.
The pros and cons of ultrafiltration systems and activated carbon devices
In the process of using the device, both kinds of pretreatment systems have advantages and disadvantages.
Ultrafiltration system
1. Advantages
The advantages of ultrafiltration systems are:
① The concentration ratio is high, and the product recovery rate can reach more than 90%;
② The clarity and quality of effluent water quality are better;
③ As a reverse osmosis pretreatment equipment, the application of ultrafiltration system can greatly reduce the investment in reverse osmosis and extend the service life of RO membrane (life span is more than 3 years);
④ The system has high degree of automation, simple structure, less operation and maintenance cost, and can be backwashed and chemical washed online;
⑤ Small footprint.
2. Disadvantages
The disadvantages of ultrafiltration systems are:
① Because the micropore size of the ultrafiltration membrane is between 0.002 and 0.1um, and the colloidal volume in water is ≥ 0.1um, the latex volume is ≥ 0.5um, the bacterial volume is ≥ 0.2um, the particle volume is ≥ 5um, the filtration range is wide, therefore, in the process of system operation, some parts are easy to be blocked, affecting the water flow rate and the service life of the membrane; (2) The initial investment is large, and the price of the ultrafiltration system with the same water yield is generally 2 to 3 times the sum of the multi-media plus activated carbon system;
③ The requirements of the ultrafiltration system on the inlet pressure are more strict;
④ Can not be shut down for a long time, if the long-term shutdown, the membrane must be sealed with pharmaceutical.
Activated carbon system
1. Advantages
The advantages of activated carbon systems are:
① the initial investment is small; The water output is stable, and the requirements for the system inlet pressure are less.
2. Disadvantages
The disadvantages of activated carbon systems are:
① Covers a large area.
② In the process of system operation, due to the participation of activated carbon and anthracite in physicochemical reaction, natural consumption increases, adsorption failure, and the quality of water production deteriorates, thus affecting the reverse osmosis system.
③ The backwash cycle of activated carbon filter is not easy to control, and the time is relatively short. Activated carbon becomes powder with the water flow out, seriously polluting the water quality and the next level of equipment. If the backwash cycle is long, the activated carbon filter is easy to form a high pressure difference, which causes the risk of system operation and affects the water output.
④ The late operation and maintenance cost of the system is high, the workload is large, and the service life of the filter material is short (it needs to be replaced once a year).